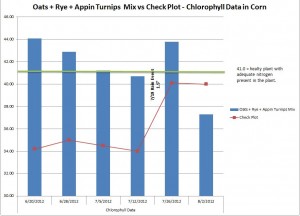
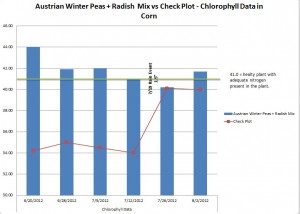
A Huge Problem

Recently I was in Minnesota with Brad Hagen, T.J. Kartes, and Andrew Heath looking at Brad’s 1,000+ acres or cover crops. Brad had not intended on planting any of theses acres to cover crops in July, 2013…his intentions were to plant them in August or early September. But spring 2013 rains and floods kept Brad from planting corn or soybeans on most of his 1,700 acres near Ellendale, MN (about an hour SW of Rochester, MN ). Brad attended a cover crop meeting TJ set up for me to speak at on behalf of Legacy Seeds last March and as I spoke I could see Brad’s mind working. When the spring rains came so did phone calls from Brad to TJ and from TJ to Andrew or me (or both)…”what can I do to build soil during this disaster?” was the theme of the weekly (if not daily) phone conversations.

Cover Crops to the Rescue!
Brad’s goals are to build soil and to scavenge nitrogen from his hog operation and build nitrogen with legumes. Realizing that we would plant in early-mid July and not in mid-late August we all understood that we did not want to have to mow to remove seed heads if at all possible – so we left Radishes out of the mix. We also realized that we wanted to use a “summer” clover, so we used Berseem Clover for it’s excellent growth and N producing ability. We chose Oats as the grass in most fields and then we added a twist, Pasja or Vivant Hybrid Brassica. I have worked with Pasja for over 10 years and rarely ever saw it produce a seed head in the summer or fall. While Pasja (nor Vivant) have a big tuber like a Radish they do have the ability to scavenge a tremendous amount of nitrogen and earthworms dwell around their roots.

In some later July (and soon to be mid-August) planted fields we chose to use Spring Barley and Crimson Clover along with PileDriver Radishes and Appin Turnips. TJ and Brad requested this mix so we’d get later fall growth, deeper penetration through compacted soils (Radish vs. Pasja/Vivant) and excellent N production from the Crimson clover. Spring Barley was available and many folks in Kentucky have told me that barley makes the soil “sweet” (whatever that means). From experience I know that soil after Barley is quite mellow.
Early August Report
From what I saw on August 1 I was very impressed! As other folks in the region were planting straight Oats or possibly a few were adding Radishes very few other folks seemed to totally share Brad’s goals. Brad told me that he is doing these cover crops because he wants to build his soil and because he wants his 7 year old son to have better soil to farm when he grows up and farms his place like Brad does with his father. I’ll have more photos in a month or so. I believe Andrew, Brad and TJ will plan a field day for September. It’s beautiful country near the Hagen farm…it probably will be worth the drive in September to meet Brad and his family. They’re pretty special folks…
Take a look at my You Tube channel “covercropdave” to watch an interview I have with Brad and TJ.