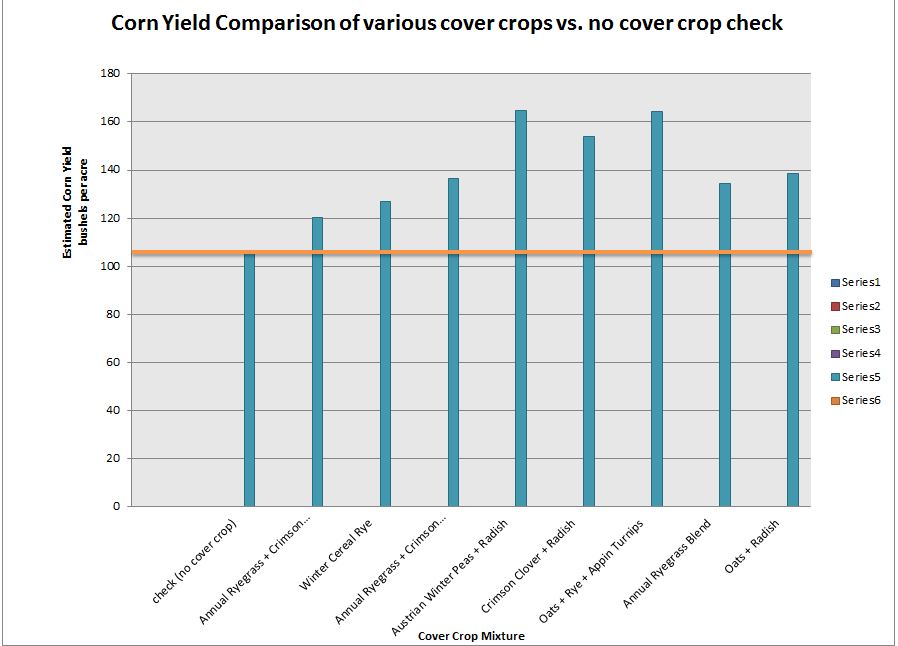
Cover Crops Provide Improved Corn Yields in On-Farm Trial
All of what is reported below was accomplished after only one year of cover crops. This work was inspired by a conversation Don and I had last winter with Dr. Eileen Kladivko from Purdue University. As I say in cover crop meetings, Don’t expect a miracle the first year – but look for one. Over […]
Cover Crops Provide Improved Corn Yields in On-Farm Trial Read More »