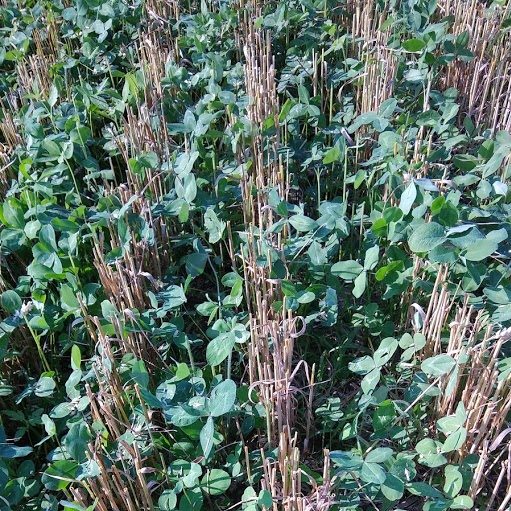
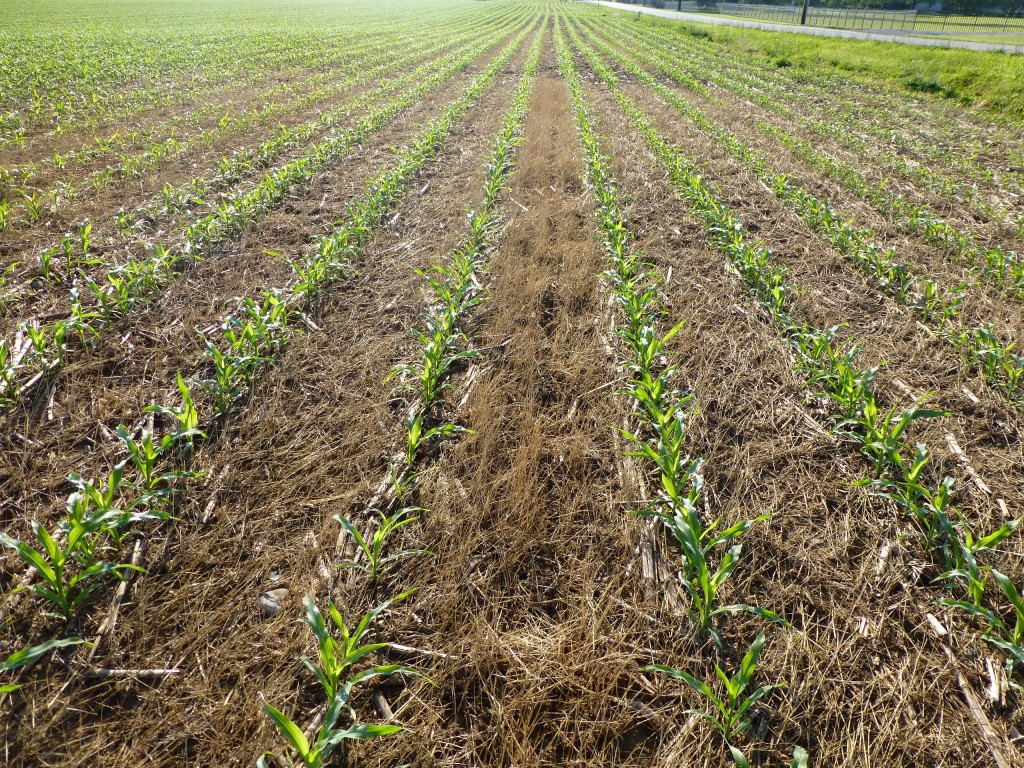
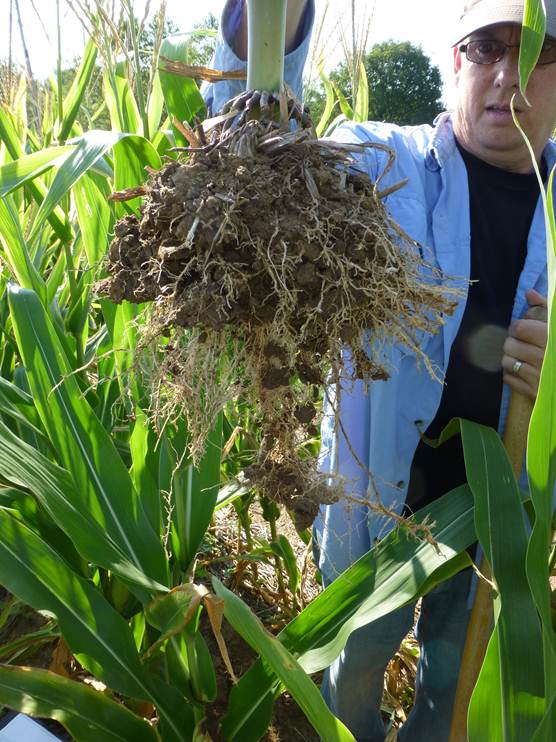
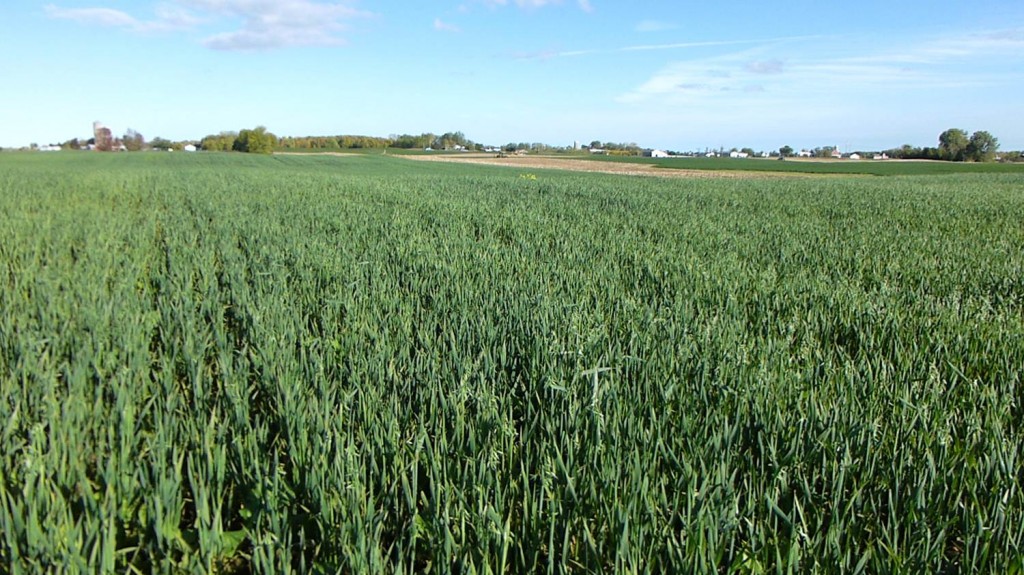
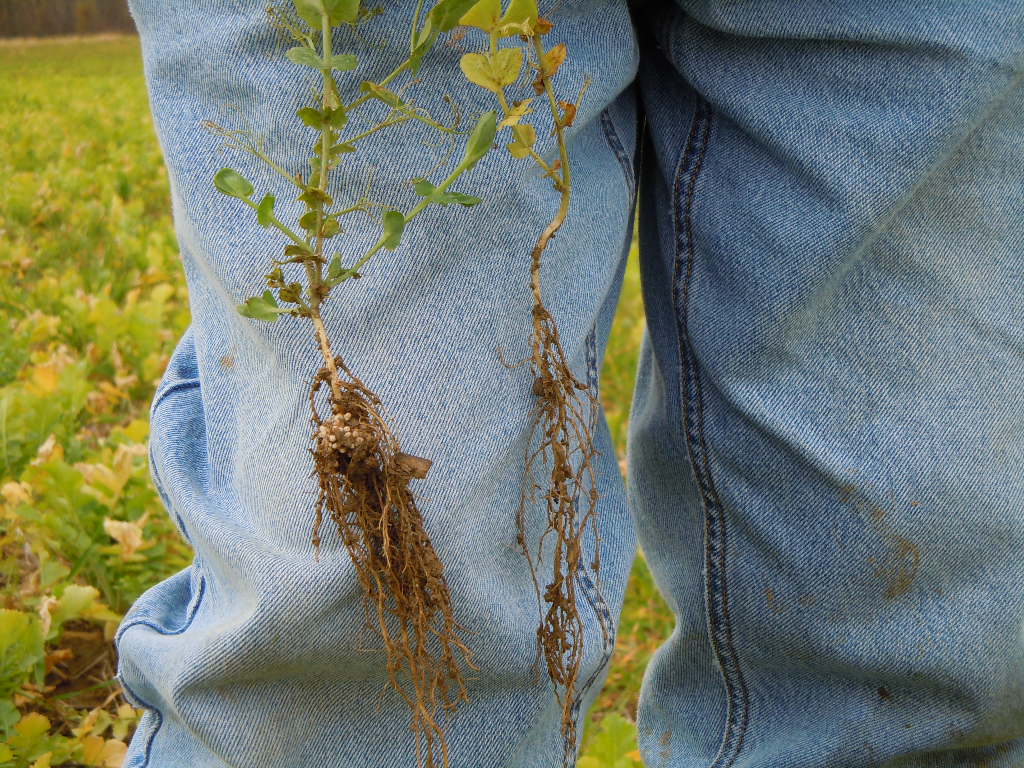
Benefits of a Pure Stand of Cover Crop Red Clover
This was my first experience growing a pure stand of red clover. The main goal for the stand was nitrogen fixation for next year’s organic corn crop.
Benefits of a Pure Stand of Cover Crop Red Clover Read More »